Environmental Benefits of EVs
Emissions from gas cars contribute significantly to atmospheric carbon dioxide and the warming of our planet.
Electric vehicles can help.
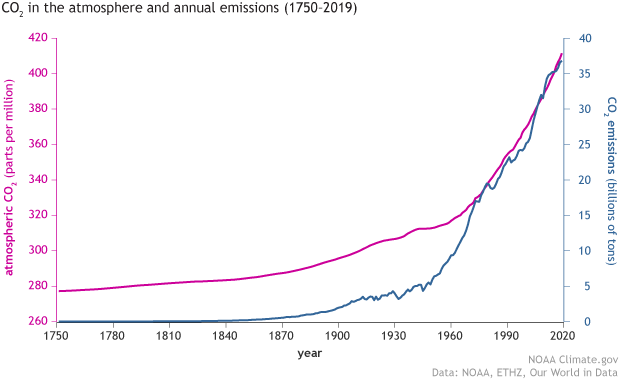
Carbon emissions on the rise…
Global warming is an existential threat and there is undeniable proof that carbon dioxide emissions contribute to it. Much of the carbon emissions that we’re pumped into our atmosphere can be traced to fossil fuels using radiocarbon dating .
Carbon emissions, particularly over the past 50 years, have skyrocketed. Transportation is a significant contributor.
The following video was created using data from NOAA’s Global Monitoring Laboratory. It highlights the increase in CO2 over the time. When Dr. Keeling started CO2 monitoring in 1958, the value was 315 parts per million (PPM). The August 2022 value was 417 PPM, according to NOAA. Contrast that with an average of 278 PPM before the Industrial Age (the period when we started burning coal).
Why Carbon Emissions Matter
As greenhouse gases collect in our atmosphere, our planet warms. This is triggering many well-known consequences, e.g., temperature extremes, super storms, flooding, droughts, and ocean acidification.
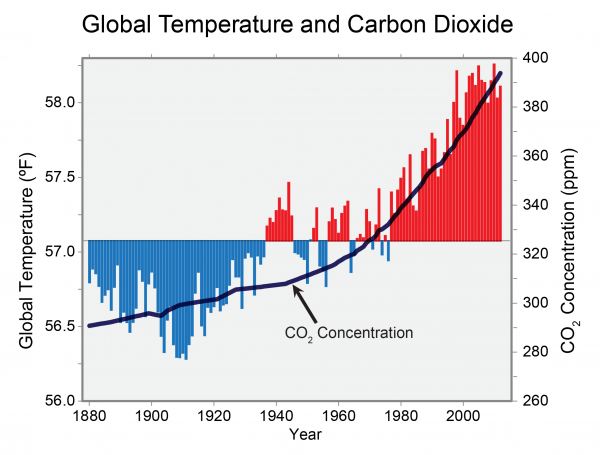
Here’s the relationship between atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration and global temperature.
Source: GlobalChange.gov
“Kick Gas” and Help the Environment
Switching from gas or diesel cars to electric vehicles allow you to reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. When you drive an EV, you to instantly help to improve our environment.
How EVs Make a Difference
EVs don’t produce tailpipe emissions that contribute to climate change and smog. They don’t emit smelly, poisonous exhaust fumes. and therefore contribute to improving public health and reducing ecological damage. The reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and air quality benefits depend on energy source of the electricity used.
Charging your EV on renewable energy such as solar or wind minimizes pollution and emissions. Those who rely on grid electricity will see benefits even if it is powered exclusively by coal.. Of course, Hawaii has a goal to transition to 100% renewable energy by 2045 and by 2019, the state had acheived 22%. As this transition happens, EVs get even cleaner.
EVs are 2-3 times more efficient than gasoline-powered vehicles. Electric cars are highly efficient - unlike gas cars where a lot of the energy is wasted as heat., most of the stored energy in EVs is utilized. Importantly, this also means that you are maximizing your ‘fuel’ dollars.
How Clean is Your EV?
Are you interested in learning about the carbon emissions associated with an EV? Use the Union of Concerned Scientists Emissions Calculator to determine emissions impact of EVs, based on car model and location.
Future Considerations
Passenger vehicles in the U.S. are electrifying at an unprecedented rate. In 2018, one million EVs were on the road, and recent studies project that by 2030, approximately 20 million EVs will be deployed across the country. Globally, this number could surpass 250 million EVs by 2030, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
With the number of EVs coming online in the coming years, it is crucial that both customers and utilities continue to explore new ways to charge EVs with renewable energy sources in order to maximize emissions reductions. EV charging can also be an important source of flexible electricity demand to enable use of larger amounts of variable solar and wind energy on the grid.
Schemes that incentivize charging during periods of peak renewable energy production have been tried locally. This includes various Time-Of-Use pilot programs that have been implemented by Hawaiian Electric. However, more robust and permanent programs are needed to maximize EV adoption, renewable energy production, and, the reduction in carbon emissions.
Inspiration can be found in other states where some utilities and EV charging providers across the U.S. are rolling out programs and services that allow EV residential and commercial customers with electric vehicle fleets to choose renewable energy for their EVs charging needs. Some allow EV owners access to a network of charging stations powered by renewable energy sources through paid subscriptions.